People invented straws in the 19th century in order to reduce the effect of oral warmth to the temperature of cold drinks. The earliest straws were made of natural plant fibers, such as rye straw and paper. However, these two had the problem of breaking down into pieces and dissolving into drinks. They were thus replaced by plastic in the 20th century. They could be rapidly produced, had lower cost and were hygiene and durable.
After almost a century of using these disposable straws, they have been found all around the environment. According to the statistics made by the Ocean Conservancy, the quantity of straws and stirring rods found in 2016 was the 6th largest of all kinds of waste. Plastic straws are easily swallowed by marine animals and can further cause ecological disasters, so people have developed eco-friendly straws as a substitute. In order to retain the advantages of safety, hygiene and convenience of plastic straws, biodegradable straws have become a magnet for people’s consumption activities. Thanks to the efforts made to replace plastic straws over the years, in 2021, the quantity of straws and stirring rods found slightly decreased to the 9th largest of all kinds of waste. In the future, it is hoped that plastic straws will disappear from people’s sight.
What are Biodegradable Straws?
Biodegradable straws are mostly designed for single use. From several months to years after use, they can be decomposed by the microorganisms in the environment and return to the Earth. By contrast, plastic straws usually take hundreds of years to decompose. Corn starch, wheat and bagasse are common plant-based materials, which are renewable and can help achieve SDG 12 “Responsible Consumption and Production” through the biomass cycle. At the same time, many biodegradable straws can provide an experience similar to using plastic straws, making them an excellent substitute for the latter.
Is Biodegradable Straw an Eco-friendly Alternative to Single-Use Plastic?
As they witness the ecological damage caused by single-use plastic straws, people have been worried about the possibility of biodegradable straws becoming the next environmental killer. In fact, biodegradable straws can be decomposed at different rates and under various conditions; not every type of biodegradable straws can be degraded in natural environments. For example, though PLA straws are biodegradable, they can only be decomposed and return to the Earth in a high-temperature composting environment, so they require industrial composting companies in the region where they are used.
Other biodegradable raw materials such as paper will release substances that are hazardous to the environment during natural decomposition after they are added with chemical additives, e.g. waterproof coatings or dyes. Hence, when using biodegradable straws as substitutes for single-use plastic straws, attention should be given to the question whether the waste management system of the using region can handle the specific biodegradable straws. Or, one could just choose the home compostable straws that are indicated as decomposable at room temperatures. However, do make sure that no chemical substance that affects the environment is added. In addition, these straws shall also be properly buried in the compost bin or soil instead of being randomly disposed. Only by doing so can biodegradable straws become the best choice for replacing single-use plastic straws.
EU Plastics Ban and Using Biodegradable Straws
In 2019, the EU started developing a policy to restrict the use of single-use plastic straws. This policy took effect in 2021. Today, the EU issues a comprehensive ban on single-use plastic straws in the market. Most operators, including Costa, Caffè Nero and Starbucks, have developed cup lids for drinking directly from a cup or bottle as well as providing biodegradable straws to meet EU laws and regulations.
Compostable or Biodegradable Straws?
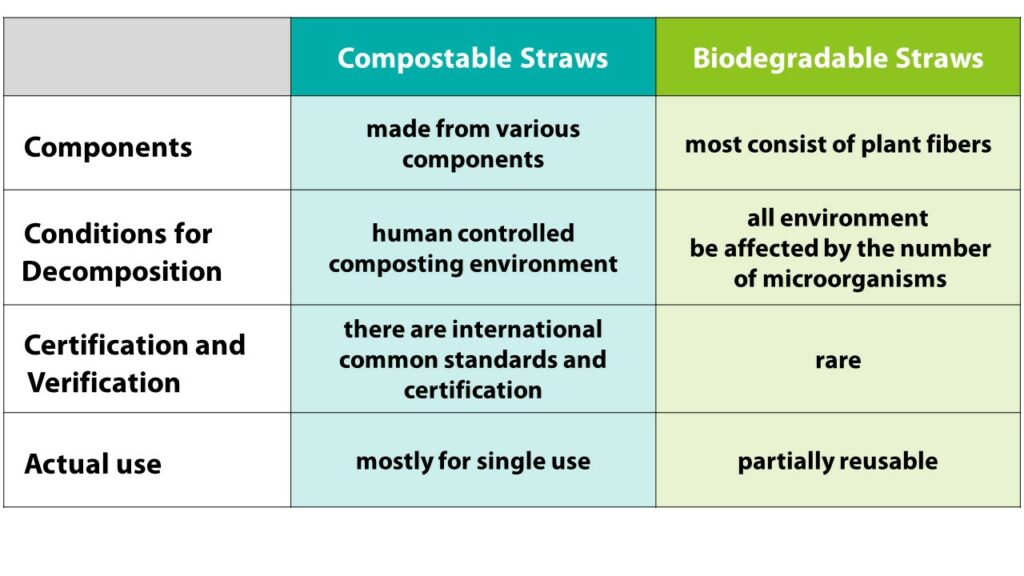
Compostable straws are a type of biodegradable straws, but the latter are not necessarily compostable. A description of components, conditions for decomposition, certification, verification and actual using status will be provided below.
Components
Compostable straws can be made from various components such as natural plants such as bagasse, corn starch, wheat straw, and also synthetic materials like PHA (Polyhydroxyalkanoates) produced by bacteria. These materials can be decomposed in a few months in a composting environment while generating carbon dioxide, water, and nutrients only. On the other hand, Most biodegradable straws consist of plant fibers such as paper, wood, and bamboo. Many reusable straws are included in this category. If a straw can be degraded in natural environments, it may be referred to as a biodegradable straw.
Conditions for decomposition
After laboratory testing, the most common conditions for decomposing compostable straws are industrial and home composting. As the main material for industrial composting, PLA straws are mature compostable straws with the highest percentage. They require large, high-temperature and centralized composting facilities as well as a temperature of 56-60°C to be decomposed. Thus, they need to be sent to industrial composting companies for decomposition. As for home-compostable products, the raw materials include bagasse, seaweed and paper. The condition for degrading them is a small composting site at a room temperature of 20-30°C, e.g. gardens, vegetable farms and compost bins at home.
Biodegradable straws can be decomposed by exposure to the wind, rain, and sun as well as erosion of microorganisms, so there is no specific standard for decomposition. However, the decomposition rate will definitely be affected in an environment that lacks microorganisms, such as deserts and cities.
Certification and verification
Compostable straws are mainly tested according to the EN 13432, AS 5810 and NF T57-800 standards. Common certifications for compostable products around the world include: Germany/the EU, the DIN-CERTCO compostable label; Belgium/the EU, the TÜV OK compost label; the US, the BPI compostability mark; and Australia, the ABA Seeding compostability mark. Each of these countries has a widely adopted certification for compostable products; however, there is no standard for certifying and verifying biodegradable straws. They are subject to the credibility of product suppliers only.
Actual use
Light, pliable yet tough and single-use, most compostable straws provide an experience similar to using plastic straws. For example, users are often confused about whether PLA industrial straws are made of plastic or compostable plastic. Biodegradable straws include not only paper straws but also reusable wood and bamboo straws. These straws are extremely different from plastic straws when it comes to user experience. For example, paper straws have the issues of becoming soft and paper-like taste while wood and bamboo straws are harder, thicker, and more solid.
5 Best Types of Biodegradable Straws
Paper straw
Paper straws have the longest history among all biodegradable straws. They mainly consist of paper pulp made of wood fibers after machining. Due to their paper-based nature, they will gradually become wet and soft when soaked in liquid. In this process, they will break down into small pieces of paper scraps and affect the experience of drinking. Thus, some paper straws are added with chemical additives such as PFAS to form waterproof coatings. However, these chemical agents might damage the body and the environment. If a paper straw has no additional chemical coating and pigment, it is one of the most easily decomposed biodegradable straws. It will be suitable for drinking drinks with a temperature of under 60°C.

Paper straws with additional pigments. Source: Flickr.
PHA straw
PHA straws are one of the latest biodegradable straws. The raw material, PHA, is produced from the fermentation of canola oil and does not contain PLA-based components. In addition, canola oil is currently the 3rd most widely produced cooking oil around the world. PHA straws are usually blue, and they can be degraded by industrial and home composting as well as in the ocean. Furthermore, they also provide an experience similar to using plastic straws.
PLA straw
Mainly consisting of corn starch, PLA straws are made with extremely mature technology for materials of biodegradable straws. They are transparent by nature, which makes them look similar to plastic straws, but they can also be colored through additional pigments. The temperature of drinks suitable for them is around 50°C. In addition, they can only be decomposed in an industrial composting environment, so they need to be handled at large industrial composting sites in the region where they are used. Otherwise, they are almost impossible to be degraded in the environment or landfills, according to the research “The Life Cycle Assessment for Polylactic Acid (PLA) to Make It a Low-Carbon Material”.
Bamboo straw
Bamboo straws are made of arrow bamboo after cutting and disinfecting, and some of the original appearance of a plant is retained. They are thick enough to be reused and do not get soft. If they enter the environment after disposal, they will naturally decompose like bamboo. Nonetheless, it should be noted that they need to be kept dry when reusing; otherwise, they will easily become moldy and unsuitable for use.

Thick bamboo straws. Source: Flickr.
Bagasse straw
Bagasse straws are made of sugarcane fibers, which are agricultural waste generated after sugar extraction. They appear to have the natural color of sugarcane and pellets of a plant. Not only that, but they also have no additional PLA and are home compostable. As they withstand a high temperature of 90°C, they do not become soft when they meet water. To take care of both the circular economy and using experience at present, bagasse straws would be a good option in the market.
For more information on eco-friendly bagasse straws along with their characteristics, please see this article: ”What is Bagasse? 6 Benefits of Bagasse for Food Packaging”
How Much does Plastic Straw Pollution Affect the Environment?
After plastic straws enter the environment, they are often swallowed by marine animals, causing injury and death to marine life. They can also block the sunlight from the ocean and further result in the death of algae. In addition to damaging marine ecosystems, plastic straws will reduce the amount of carbon dioxide stored in the ocean and aggravate the greenhouse effect. The impact of them is even more severe than the shocking photo of this well-known, poor turtle.
How Long do Biodegradable Straws Take to Decompose?
There is no common standard for testing biodegradable straws. Thus, the decomposition time will be affected by the design of the straw as well as the environment for decomposition. However, based on the current consensus on biodegradable straws, most of these straws can be decomposed in common environments with abundant moisture and microorganisms (e.g. forests, grasslands and flower gardens) within a few months.
The Future of Biodegradable Straws
Considering that the development of biodegradable straws continues to boom, the world is paying close attention to their future. For example, the EU has been widely discussing issues of biobased, biodegradable and compostable plastics. At the end of 2022, it developed the policy framework for the future. The major goal is to adopt more secondary materials, including bagasse, for production while ensuring that biodegradable straws can be properly handled after use without causing environmental issues.
For more information on the pros and cons of biodegradable straws and more policy information, please read this article: 6 BENEFITS OF BIODEGRADABLE STRAWS ARE BETTER FOR THE ENVIRONMENT.
Conclusion
Biodegradable straws are one of the best substitutes for plastic straws. They offer safety, hygiene and convenience while being friendly to the environment. With the flourishing development of technology, biodegradable straws that easily degrade and do not contain additional chemical substances, such as paper straws without bleaching and chemical coatings, bamboo straws or bagasse straws, are good options.














