The use of straws has become part of people’s daily life. Made of plastic, most straws have the advantage of being tough yet light and hygienic in the past. However, they were hard to recover and required hundreds of years to decompose due to these characteristics. They not only caused environmental issues after entering the environment or accumulating in landfills, but also broke down into microplastics during the decomposition process. This caused even greater damage to ecosystems. According to statistics, around 63 to 142 billion straws were used in the US in 2017. Meanwhile, 36.4 billion straws were used in the EU countries. These are extremely enormous numbers. Degradable in the environment, biodegradable straws have become a new consumer trend around the globe in the hope of solving the issue of single-use straws. This article will introduce biodegradable straws with an explanation of what they are, their characteristics as well as advantages and disadvantages.
What is Biodegradable Straw?
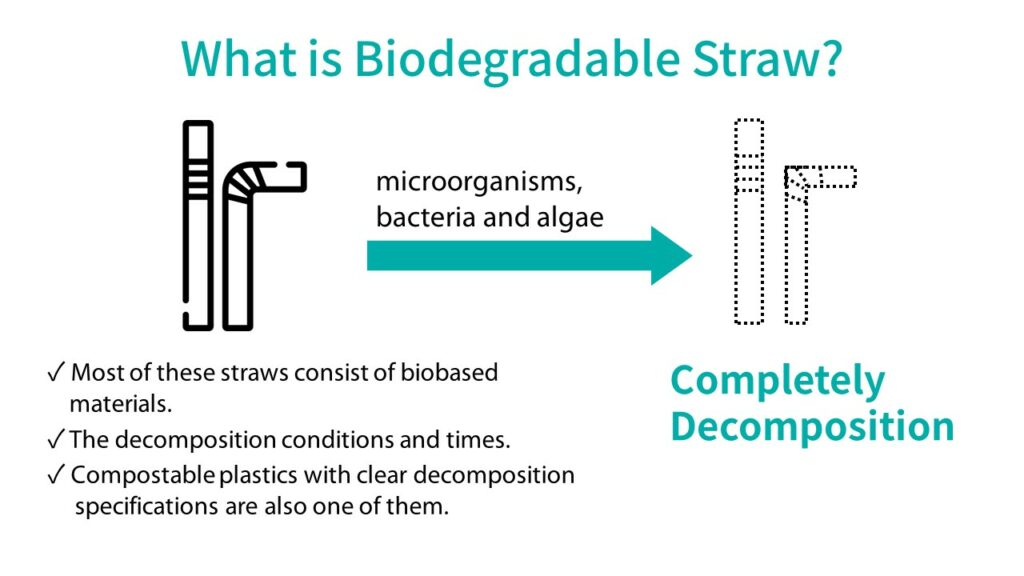
After use, biodegradable straws can be decomposed by microorganisms, bacteria and algae that naturally live in the environment. Most of these straws consist of biobased materials including bagasse, rice hulls, wheat or corn while some others are made of fossil-based materials. However, the decomposition conditions and times vary due to different manufacturing methods and materials. In order to regulate biodegradable straws, economies such as the US and the EU have established standards including the ASTM D6400 and the EN 13432. As a result, “compostable plastics” that can be decomposed in a certain time under specific conditions have been further divided from the field of biodegradable materials.
Biodegradable Straws are Eco-friendly Alternative to Single-Use Plastics
In 2015, the sea turtle conservation group the Leatherback Trust released an appalling video of pulling a plastic straw out of the nose of a sea turtle. Shocked, people realized the harm that single-use plastic straws can bring to the environment. Considering the demand for safety, hygiene and convenience when drinking beverages, biodegradable straws would be the hope to replace single-use plastic straws and reduce the damage to the environment after using straws while maintaining the help of single-use plastic straws to the daily life.
6 Benefits of Biodegradable Straws
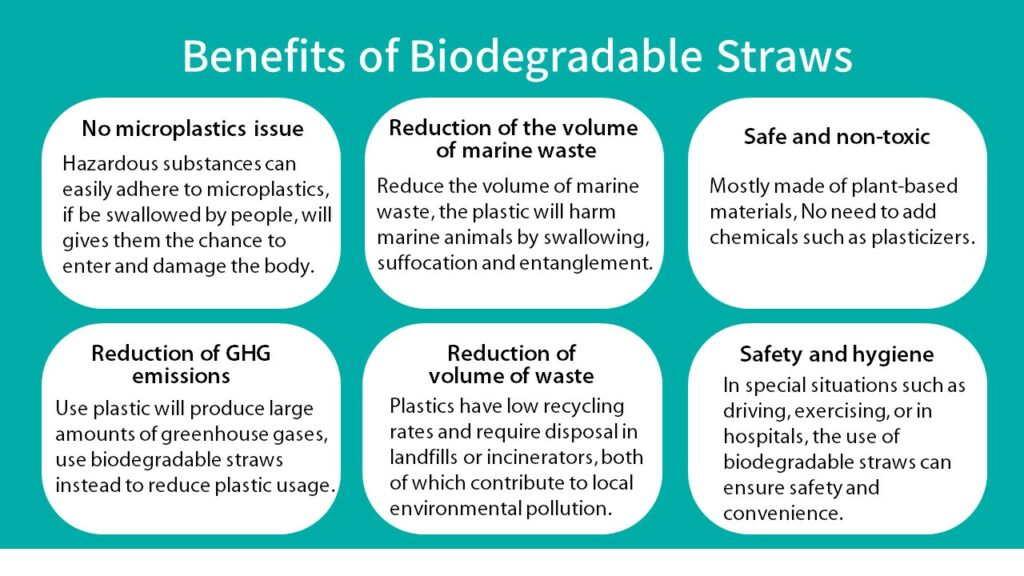
No microplastics issue
After plastic enters the environment, it will gradually become brittle, degrade and break down in the sunlight. These broken plastics will turn into microplastics and reach every corner in the world through the water cycle, including rivers, lakes, and the oceans. Accumulated in the body of animals in these environments, the microplastics will eventually be swallowed by people along with fish, shrimp, and shellfish. Hazardous substances (e.g. heavy metals) can easily adhere to these microplastics, and this gives them the chance to enter and damage the body. By contrast, biodegradable straws can be naturally decomposed in the environment instead of becoming microplastics and getting in the body.
Reduction of the volume of marine waste
In accordance with the statistics made by the International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources (IUCN), at least 14 million tons of plastic enter the ocean each year, accounting 80% of all marine waste. Most of these plastics are unproperly disposed waste from the land that entered the ocean through rivers or groundwater. They can harm marine animals by swallowing, suffocation and entanglement. Hence, the use of biodegradable straws can reduce the volume of marine waste as well as the negative impact on marine ecosystems caused by people.
Safe and non-toxic
Biodegradable straws are mostly made of plant-based materials, so they hardly generate toxic substances. On the contrary, plastic straws may contain chemical additives such as heat stabilizers, ultraviolet stabilizers, colorants and plasticizers during the manufacturing process, and these could be released due to abrasion, temperature changes or erosion of acid drinks when using the straws. At present, it is uncertain if these substances will harm the body over time, so biodegradable straws would be a safer choice.
Reduction of greenhouse gases (GHG) emissions
The source of plastic is petrochemical raw materials. First of all, crude oil needs to be transported from oil-producing countries to other countries across the ocean. After it is thermally fractionated and cracked in local processing plants, the plastic materials generated will be delivered to plastics manufacturing factories and then made into all kinds of plastic. This transportation and manufacturing process will produce large amounts of greenhouse gases (GHG). The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) pointed out that in 2019, 18 billion tons of GHG were generated from plastics, which was 3.4% of the total GHG emitted globally. It is expected that 43 billion tons – more than twice the number at present – of GHG will be produced from plastics in 2060. This will further cause climate change. By using biodegradable straws, the demand for plastic can be reduced and further resulting in the decrease of GHG emissions.
Reduction of volume of waste
The issue of waste is facing every country around the world. Most waste enters landfills or incinerators and then causes soil, water, and air pollution during the handling process of decomposition or burning. Therefore, both facilities are NIMBY (not-in-my-backyard) for local residents. According to the OECD’s statistics, the recovery rate of global plastic waste only reaches 9%. Furthermore, small single-use plastic straws are almost impossible to recycle for reuse. As a result, biodegradable straws can help reduce the amount of waste and further mitigate the global waste problem.
Safety and hygiene
Besides biodegradable straws, one can also use reusable straws that can be recycled and made into other products, or cut the use of straws and drink from the cup directly. However, as reusable straws are made of stainless steel or glass, there might be safety concerns while carrying or using them, and they need to be cleaned properly to ensure good hygiene. Additionally, in special situations where drinking from a cup is not ideal, such as driving, exercising, or in hospitals, the use of biodegradable straws can ensure safety and convenience.
Pros and Cons of Biodegradable Straws
With the advantage of being safe, hygienic, eco-friendly and convenient, biodegradable straws are one of the best substitutes for single-use plastic straws. Although, they do have some disadvantages. For example, biodegradable straws made of some materials including paper and pasta, will provide unnatural and negative taste such as paper-like, metallic, and wheat-like taste, affecting the experience of drinking beverages. In addition, most biodegradable straws can only be stored for 1 to 3 years whereas plastic straws are able to last more than 10 years. After the expiration date, biodegradable straws will become brittle. Hence, if a person or an operator is to purchase biodegradable straws, they should estimate their own usage, adopt the “pay-as-you-grow” method and buy straws in small quantities.
EU Plastics Ban and Using Biodegradable Straws

The EU announced the “DIRECTIVE (EU) 2019/904 OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL of 5 June 2019 on the reduction of the impact of certain plastic products on the environment” in 2019. This Directive aims to reduce the volume of waste produced, so it is applicable to some (if not all) single-use products (SUP) made of plastic or oxo-degradable plastic. These products are usually used once, or disposed of after a short period of use. Tableware, plates, straws, cotton swabs, instant meal boxes and drinking cups are all included in the prohibited items. As for single-use plastic straws, the use of them has been officially banned since July 2021. Currently, biodegradable straws such as paper, wheat and bagasse straws are the major substitutes on the market.
Are Biodegradable Straws Better for The Environment?
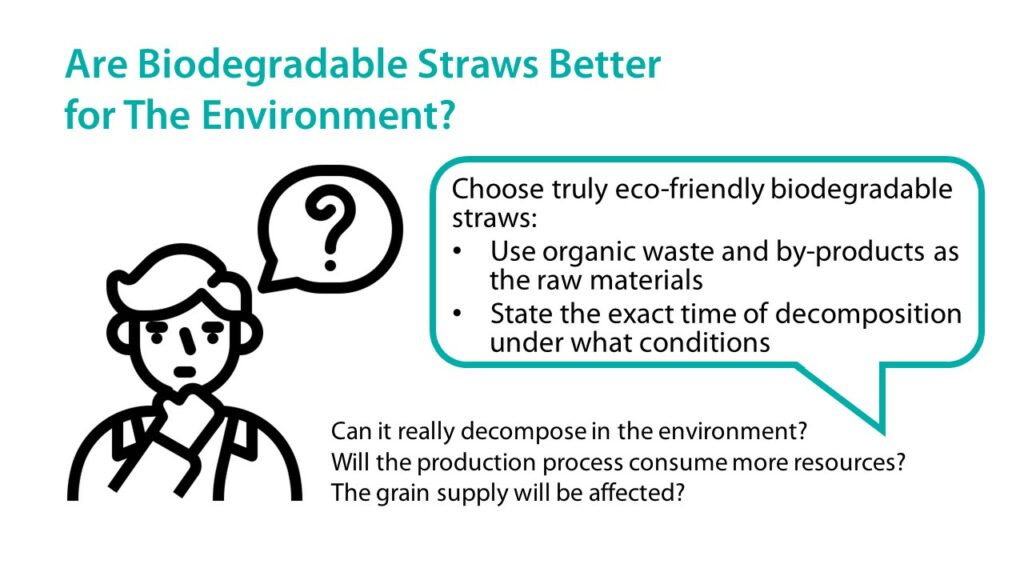
Biodegradable straws have aroused many environmental controversies after launch, including whether they can be decomposed naturally in the environment, or if the manufacturing process consumes more resources. “Biodegradability” is just a concept that is not subject to substantive norms. Thus, some suppliers’ so-called “biodegradable straws” have not undergone decomposability tests, and it is uncertain how long it takes for them to decompose. Unscrupulous operators may mix plastics into their biodegradable straws, which will cause even more damage to the environment. In addition, the raw materials of biodegradable straws are all-inclusive; from cash crops such as corn starch and wheat to agricultural by-products including bagasse and rice hulls, these are all common raw materials. If additionally grown cash crops are required, then the grain supply will be affected.
Today, every country has started establishing laws and regulations with respect to these issues. For example, the “European Green Deal: Putting an end to wasteful packaging, boosting reuse and recycling” published at the end of 2022 indicated that in the future, the EU will require producers to use organic waste and by-products as the raw materials first. Moreover, it will force the indication of the time needed for biodegradation in any environment on biodegradable materials. If secondary materials of the agriculture industry (e.g. bagasse) are used, or if the degradability is ensured by passing certifications for compostable products (e.g. the BPI, DIN CERTCO and TUV), biodegradable straws would be a more eco-friendly option.
FAQs for Biodegradable Straws

How long will a biodegradable straw degrade in natural environments?
Biodegradable straws, for the most part, only require a few months to degrade in natural environments. This depends on the actual status of the environment and the composition of raw materials. In warm, moist, and microorganism-rich soil environments, the decomposition rate of the straws will be faster. Other than that, the rate also depends on whether materials that are harder to decompose in normal environments are added. For example, straws with PLA degrade much slower in normal environments; they can only be rapidly decomposed in an industrial composting environment at around 58°C.
What is the best way to dispose biodegradable straws?
Whether a biodegradable straw enters the natural environment that meets its requirement for degradation cannot be ensured. Therefore, random disposal of biodegradable straws might still harm the environment. As a result, the best way to dispose biodegradable straws is composting. Industrial straws must be recovered and sent to industrial composting companies pursuant to the regulations made by local governments. On the other hand, home compostable straws can be one of the materials for home composting and directly buried in the yard at home or put in compost bins.
What is the difference between biodegradable straws and compostable straws?
Biodegradable straws are simply a kind of straw that suppliers claim to be degradable in natural environments, but they are not necessarily tested. Thus, the composition of the raw materials as well as the condition and time of decomposition are uncertain. If a biodegradable straw has been strictly tested with explicit standards, it may be referred to as a compostable straw. The safety and eco-friendliness of this kind of straw are better ensured.
Are biodegradable straws good to use?
Biodegradable straws are just as useful as single-use plastic straws if PLA, which is made of corn fibers, is used as the material. Not only the physical nature, but even the appearance is similar to that of plastic straws. However, the disadvantage is that PLA straws only meet the decomposition standard of industrial composting, so they must be specifically delivered to industrial composting companies for handling. As a result, Renouvo and some other companies use bagasse, a secondary material of the agriculture industry, as the material and launched PLA-free biodegradable straws. These can provide a user experience similar to single-use plastic straws while better meeting the standards for home composting as they can degrade at room temperatures.
How many people are using biodegradable straws?
Based on the statistics provided by Future Market Insights, the size of the global eco-friendly straw market is expected to reach USD 10.71 billion in 2023. Many well-known chain businesses including Costa, Caffè Nero, Dunkin’, Starbucks, McDonalds and MOS Burger have started to offer biodegradable straws in some of their stores. This means that biodegradable straws have entered the daily life of the general public.
For The Environment, Where do We Get Biodegradable Straws?
As single-use plastic straws cause global warming and garbage pollution, their impact can be reduced by using biodegradable straws. Consumers may visit the stores where biodegradable straws are provided, or bring their own reusable eco-friendly straws. On the other hand, catering operators which provide drinks can buy biodegradable straws to fulfill their ESG obligations. In addition, B2B sales and services are adopted for several kinds of biodegradable straws. For example, Renouvo offers home compostable straws made of agricultural waste (bagasse), which are safe, eco-friendly, convenient, and compliant with laws and regulations of each country.














