As countries worldwide are reducing plastics or stipulating regulations to limit plastics, a wide range of compostable products has emerged on the market. Besides general compostable products that are free from chemical treatment and made from natural materials, third-party organizations with international credibility have also launched compostability certification labels to ensure the compostability and safety of emerging materials that have undergone physical or chemical treatment. Choosing products with compostability labels allows consumers to enjoy the benefit of convenience while being eco-friendly. This article will elaborate on the characteristics of compostability and the most common certification labels on the market, as well as introduce the advantages and composition of 18 compostable products in order to help readers get to know more compostable products.
What is compostable?
The term compostable is often used to describe materials or products that can be completely broken down into water, CO2, and nutrients in an artificially controlled composting environment. These substances are friendly to the environment and essential to plant growth. Therefore, composting is beneficial for crops or gardening, making it an eco-friendly adjective.
What’s the difference between compostable and biodegradable? For a detailed introduction to compostability, please see: COMPOSTABLE MEANING: ACTUAL COMPOSTABLE PRODUCTS.
What are the features of compostable products?
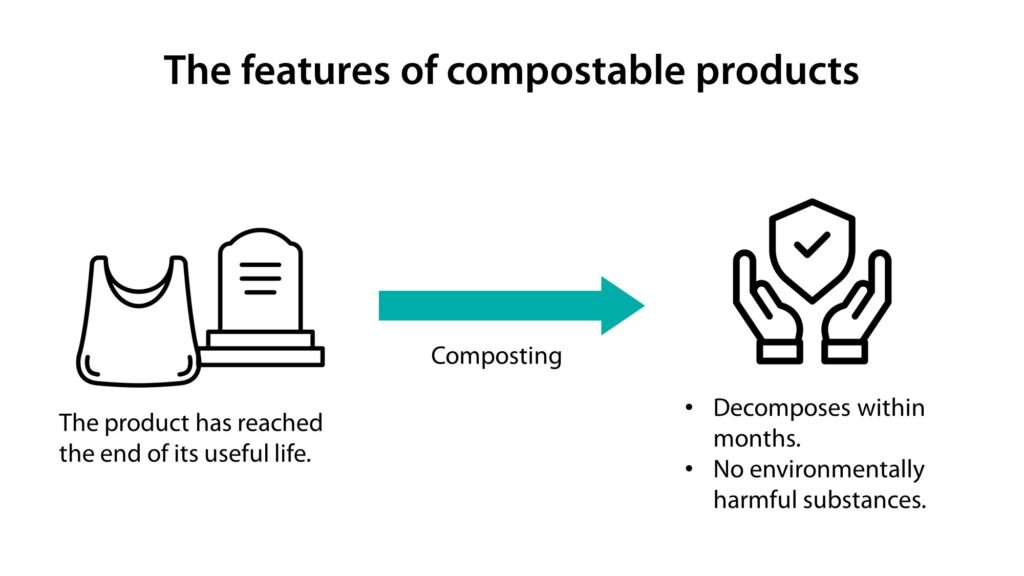
Compostable products are made from polyesters, plant fibers, or paper, and they are designed with compostability in mind. When the products reach the end of their life, they can be disposed of via composting in an artificially designed composting environment. Usually, they decompose within several months and do not produce substances that will harm the environment. Most compostable products are light and thin to facilitate decomposition, and they are mainly manufactured with biomass materials. The most common products are disposable straws and food containers such as tableware and cups.
Identifying compostable products and packaging
Since composting is an artificially controlled behavior under specific environmental conditions, simulated composting environments can be created in the laboratory to test whether products that claim to be compostable do break down in the composting environment. There are numerous compostability standards on the market, including the most common EN 13432 and ASTM D6400 that require compostable products to completely break down in an industrial composting environment within 180 days, or 360 days in a home composting environment, and the decomposed substances must not be harmful to the environment.
Compostable product certification labels are divided into industrial compostability certification and home compostability certification to indicate whether the product can be broken down in an industrial or home composting environment.
please read this article: “Commercial Composting: Commercially Compostable Products and Packaging” on the differences between industrial composting and home composting environments).
The tests are carried out by credible laboratories, and the test results are submitted to the certification organization to apply for the product compostability certification label. The seven most common product compostability certification labels are briefly introduced below:
BPI COMMERCIAL COMPOSTABILITY CERTIFICATION
The BPI COMMERCIAL COMPOSTABILITY CERTIFICATION SCHEME primarily adopts the American Society for Testing and Materials ASTM D6400 and ASTM D6868 standards, which are widely recognized by various industrial composting facilities in North America and comply with compostability certification-related regulations in various states in the US.
Official website of BPI COMMERCIAL COMPOSTABILITY CERTIFICATION
TÜV AUSTRIA OK compost INDUSTRAL
The TÜV industrial compostability certification is based on the TÜV AUSTRIA Certification Scheme: The OK compost INDUSTRIAL certification uses EN 13432: 2000 as reference, and all certified products must comply with the requirements of the EU Packaging Directive (94/62/EEC). This is widely used in Europe.
Official website of TÜV AUSTRIA OK compost INDUSTRIAL
ABA Seedling Composting logo
The ABA industrial compostability certification is a Commercial COMPOSTABLE Verification Programme launched by the Australasian Bioplastics Association (ABA) based on the Australian Standard 4736-2006. The system is referred to as the Seedling Logo in Australia and New Zealand, where it is widely used.
Official website of ABA Seedling Composting logo
DIN CERTCO DIN-Geprüft industrially compostable
The DIN CERTCO industrial compostability certification is implemented based on standard certifications such as EN 13432, DIN EN 14995, ISO 17088, ISO 18606, and AS 4736. Other standard certifications are sent to other organizations to obtain the industrial compostability certification of various regions at once.
Official website of DIN CERTCO DIN-Geprüft industrially compostable
TÜV AUSTRIA OK compost HOME
The TÜV home compostability certification is based on the TÜV AUSTRIA Certification Scheme: The certification launched by OK compost HOME includes multiple home compostability standards such as Australia’s AS 5810, France’s NF T 51800, and Europe’s prEN 17427.
Official website of TÜV AUSTRIA OK compost HOME
ABA Home Compostable Verification
The ABA home compostability certification is based on the Home COMPOSTABLE Verification Programme and certified according to Australian Standard 5810-2010, which is widely used in Australia and New Zealand.
Official website of ABA Home Compostable Verification
DIN CERTCO DIN Tested – Garden Compostable
The DIN CERTCO home compostable certification is based on the NF T51-800 standard test, which proves that the material can be safely used for home or garden composting. Meanwhile, the AS 5810 earthworm toxicity test can be included if necessary to meet the ABA home compostability certification standard.
Official website of DIN CERTCO DIN Tested – Garden Compostable
18 compostable products and their benefits
Compostable sponges
Sponges are an essential kitchen cleaning product for wiping the countertop, absorbing excess fluid, or washing dishes. Initially, sponges were made of sponge animals, but they were subsequently replaced by foamed plastic polymers due to cost and usability considerations. However, microplastics may be produced while scrubbing with sponges, and they cannot be recycled after being discarded. Compostable sponges are made of cellulose such as hemp, coconut shell, and wood pulp to ensure that there no plastic fragments are left in the kitchen during use. If the sponges are damaged or become dirty after use, they can be disposed of through household composting. However, eco-friendly dish detergents are recommended to prevent leaving harmful chemicals in the compost. Also, cut the sponge into small pieces before putting it in the compost bin to speed up the decomposition process.
Compostable straws
Straws are one of the most common disposable plastic products used by people every day. Various materials such as paper, bagasse, bamboo, cattail grass, and wheat stalks can be used to make compostable straws that can be composted in an industrial or home composting environment together with the beverage residue (depending on the manufacturer’s instructions). Currently, odor-free compostable straws that do not soften easily are already available on the market, and they are made of agricultural waste to ensure low carbon emissions and eco-friendliness. An example is:
Compostable tea bags
For people who wish to quickly brew a cup of tea, tea bags are an excellent choice as no teapot or filter is needed. Simply place the tea bag into the mug, add hot water, and wait for a few minutes to enjoy a steaming cup of aromatic tea. However, most tea bags are bonded together with plastics that may end up in our bodies. Compostable tea bags are made of materials such as PLA or organic cotton that can be disposed of with the tea leaves using industrial or home composting methods.
Compostable cling wrap
Cling wrap is used to preserve food and minimize food waste. However, it is thin and easily contaminated by food, making it virtually impossible to recycle, and it is often accidentally ingested by marine life. Compostable cling wrap is made from a combination of PLA and PBAT, hence it can be composted at home.
Compostable coffee filters
Coffee filters are made from paper pulp, and paper that has not been bleached or chemically treated is a good carbon-rich compost material that can be home-composted together with the coffee grounds from brewing coffee.
Compostable loofah sponges
Are there other useful dishwashing tools besides sponges? Dried loofah is an excellent alternative! After the loofah is sun-dried, cut, and deseeded, the remaining yellow loofah fiber can be used to scrub dishes effectively. When it gradually becomes dirty or fragile, simply cut it into pieces and toss it into the home composting bin to decompose naturally.

Loofah, Image: Flickr
Compostable cleaning cloths
Compostable cleaning cloths are made of viscose synthesized from wood pulp cellulose and protein. Although it is a type of synthetic fiber, it is still compostable. However, chemical washing, dyeing, and so on should not be carried out during the production process. After the cleaning cloths are gradually worn out, they can be used as a home composting material.
Compostable cotton buds
Cotton buds are one of the most common sanitation products used daily. Compostable cotton buds replace plastic stems with bamboo stems and unbleached cotton is used, hence the entire cotton bud can be home composted. However, if cotton buds are used to apply chemical cosmetics or nail polish, they will be contaminated and thus cannot be safely composted.

Cotton swabs with stems made from plant fibers, Image: Flickr
Compostable tableware
It is inconvenient to carry reusable tableware when dining out, while restaurants also provide disposable tableware due to hygiene considerations. Compostable tableware turns disposable tableware into a healthy and eco-friendly alternative. At present, most compostable tableware is made of PLA, bagasse, and bamboo fibers, and many manufacturers have obtained compostability certification, meaning that the products can be disposed of via industrial or home composting after use.
Compostable coffee pods
Coffee pod machines made their way into people’s lives three decades ago, with Nespresso being the most prominent manufacturer. However, since disposable coffee pods are made from aluminum and plastic, it is difficult for users to cut open the coffee pods to recycle coffee grounds and pods separately, hence they are widely criticized for being eco-unfriendly. Now, manufacturers have unveiled plant-based polyesters and paper as substitutes for plastic pods and lids, making the entire pod compostable, and they have obtained BPI industrial compostability certification. After brewing a cup of aromatic coffee, simply throw the coffee pods into the compost bin and send it to a commercial composting facility for disposal.
Compostable lunch boxes
When buying takeout, paper or plastic lunch boxes are used. However, the paper, although theoretically compostable, is often coated with a layer of polyethylene (PE) to achieve water and oil resistance, thereby creating health and environmental concerns. Compostable lunch boxes are made from plant fibers such as palm leaves, bamboo, and bagasse, which possess the natural water and oil-resistance properties of plant fibers. At the same time, they can be returned to the soil via industrial or home composting, depending on the lunch box’s certification.
Compostable dryer balls
Dryer balls increase air circulation in the dryer by rolling to reduce the drying time, endow clothes with fluffiness, and reduce the amount of fabric softener needed, making them an eco-friendly and energy-saving product. Made from pure wool, dryer balls can be cut into little pieces and composted at home after they become worn out. Remember not to add harmful chemical fragrances when using the dryer balls to prevent contaminating them, as they will release harmful substances during the composting process.

Dryer balls, Image: Flickr
Compostable poop bags
Although animal feces may contain pathogens that makes them unfit for home composting, some major commercial composting facilities are capable of composting cat or dog droppings. Compostable poop bags with industrial compostability certification are synthesized from corn, vegetable oil, PBAT, PVA, or plant starch, so they can be dropped into municipal compost boxes that accept feces.
Compostable food waste bags
People generate a large amount of food waste every day. According to the World Bank’s statistics, food and green waste account for half of the total waste generated by people. Compostable food waste bags are made from plant starch, wood pulp, lactic acid, or soy protein, which helps to collect food waste and minimize the need to clean containers. Most industrial composting facilities accept compostable food waste bags that have been certified as industrially compostable, hence they can be disposed of via the municipal food waste recycling mechanism.
Compostable toothbrushes (partial)
Toothbrushes are an indispensable consumable in everyday life. Compostable toothbrushes employ bamboo handles instead of plastic ones, hence the handles can be composted at home. Unfortunately, no compostable material has yet been developed for the bristles, but at least the goal of plastic reduction has been achieved and more substances can be returned to the soil via composting, making compostable toothbrushes a more eco-friendly alternative.

wooden handle toothbrush, Image: Flickr
Compostable flower pots
Compostable flower pots are composed of coconut shells, feathers, rice husks, as well as processed cow dung or paper pulp. Mainly used for cultivating woody plant saplings, these flower pots can be buried directly into the garden soil when transplanting the plants in the future. When growing, the plants’ roots will penetrate the flower pots and into the surrounding soil. Please note that since they are used for home gardening, it is imperative to avoid flower pots that claim to be industrial compostable as the garden soil at home will certainly not be able to provide suitable decomposition conditions.
Compostable cups
Takeout beverage cups for tea, soda, or coffee are usually paper cups with plastic coating or plastic cups. Plastic-coated paper cups require special equipment to separate the coating from the cups before they can be recycled, while recycled plastic cups cannot be remanufactured into food packaging due to hygiene considerations. As a result, it is regarded as downgraded regeneration and fails to achieve complete resource recycling. Compostable cups are made of PLA, bagasse, or paper with a plastic-free water-based coating. After use, they can be disposed of via industrial or household composting methods and completely returned to the environment.
Compostable mulching film
Mulching film helps to retain the soil’s moisture and inhibit weed growth, thus it is a frequently used product in modern agriculture. However, plastic mulching film becomes worn out due to sun exposure and releases microplastics. Also, the mulching film cannot be recycled after the crops are harvested because it is covered in soil. Compostable mulching film made from corn starch can be broken down during use, and it can be mixed into the soil with an adequate amount of agricultural waste after the harvest as compost to initiate a new round of cultivation.
3 points for choosing compostable products

Is it necessary to use compostable products?
Although compostable materials present an eco-friendly solution, they must be applied to lightweight, thin products or products composed of composite materials to realize the maximum benefits. For example, lightweight straws, mulching film, or food waste bags allow compostable products to decompose. Compostable materials are suitable for products made of multiple materials such as cups, lunch boxes, and coffee pods, or products that may have food residues on them. This can reduce the additional costs and technical challenges associated with separating and processing these materials.
Has the product passed compostability certification?
Compostability certification involves simulating the decomposition conditions of products in common composting environments in a laboratory setting, as well as analyzing the composition of the compostable product to ensure their degradability. At the same time, it also serves to guarantee that no harmful substances are created after decomposition. Consequently, a product that has passed compostability certification means that it can be completely broken down in a specific composting environment and that it can be disposed of in this way.
Is the product made of compostable materials?
Compostability certification stipulates a certain amount of decomposition time; for instance, home composting requires at least 90% decomposition within a year. Although some products are made from degradable plant fibers, due to the excessive thickness of the material or the characteristics of plant fibers, they may need a longer time to completely break down if left unprocessed. However, if they are given sufficient time, or if they are pre-processed by cutting, these products can still be composted. In other words, even if a product does not have compostability certification, one can decide whether to use it by examining whether it is manufactured with compostable materials.
Using compostable products is a way of eco-friendly living
People’s pursuit of quality of life and convenience has pushed the envelope of technological development. However, such development has also caused great harm to the Earth’s environment. The most eco-friendly approach is to return to the basics and minimize the use of various consumer products. Nonetheless, most people still wish to strike a balance between environmental protection and convenience in life, and compostable products are one of the most ideal solutions to help us realize more possibilities. Who says environmental protection and quality of life must be mutually exclusive?


















