People’s survival relies on various natural resources, which are currently in short supply. Whether it is renewable or non-renewable resources, they are bound to run out at the present rate of depletion. Whether people will survive in the future depends on the sustainable use of natural resources. This article will explain the types of natural resources and their importance, and offer enterprises five techniques to utilize resources in a sustainable manne
What are natural resources? Why are they important?
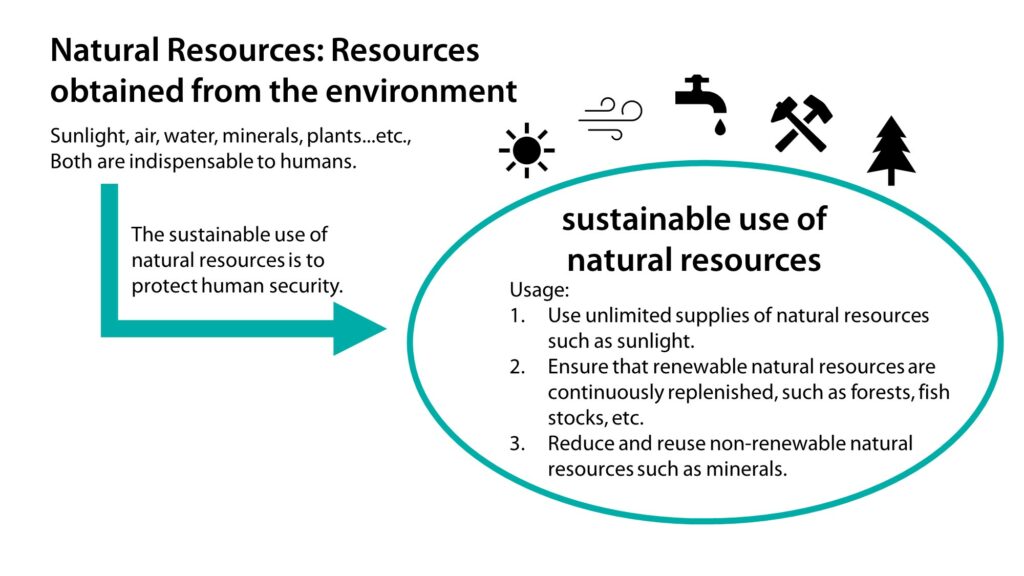
Resources obtained from the environment are part of natural resources. These include sunlight, air, and water—the three essential elements of life—as well as the soil under our feet, raw materials and minerals for industrial components, the fossil fuels that drive civilization, and animals and plants that we eat as food. Everything in our lives is made up of natural resources; lacking natural resources of any kind will have a significant impact on people’s lives.
The importance of natural resources to us is especially poignant in recent years. According to the World Health Organization’s (WHO) statistics, air pollution causes the premature death of seven million people annually, and 99% of the air we breathe contains high levels of contaminants that exceed the WHO’s guidelines. Besides the lingering toxic substances over cities and industrial zones that never dissipate, seasonal smog is now also a major problem, affecting health, lowering visibility, paralyzing traffic, and leading to accidents. These include the smog that sweeps across China, South Korea, Japan, and Taiwan in spring in the northern hemisphere, as well as the wildfire seasons in North America and Australia. If a reduction in natural resources such as air can have so much adverse impact on people’s lives and safety, we must engage in the sustainable use of resources to ensure our safety and quality of life.
What is the sustainable use of natural resources?
To achieve the sustainable use of resources, the most direct definition is that the depletion rate of natural resources must be smaller than or equal to the rate of natural resource regeneration. For instance, sunlight is a form of unlimited natural resource, so it will never run out no matter how we use it. If sunlight is used to substitute other resources, it will be a sustainable way of utilizing natural resources.
Although natural resources such as forests and fish are limited, they can be regenerated naturally or artificially. If we use such natural resources through sustainable forestry or sustainable fishing to make sure that every tree we fell and every fish we catch can be replenished in the next life cycle, it is also a form of sustainable resource utilization. However, it is not as simple as planting one tree after cutting one down or catching a limited quantity of fish. Rather, the entire ecosystem must be taken into consideration to prevent unanticipated factors such as pests, fires, and water pollution from eventually causing the unsustainable use of natural resources.
Mineral and petrochemical raw materials such as steel, copper, gold, silver, aluminum, oil, natural gas, and uranium, as well as other common raw materials and fuels in our lives, are non-renewable resources that will deplete over time and cannot be used sustainably. People can only maximize the benefits of these natural resources through recycling and decreasing consumption. In the future, we still need to look for sustainable natural resources that can be used as substitutes.
What are unsustainable natural resources?
Non-sustainable natural resources are divided into two categories. One is non-renewable resources that will eventually be exhausted; the other is renewable natural resources that are not managed appropriately. Although these natural resources can be used sustainably, they are gradually being depleted because of our misuse.

Improper use leads to unsustainable use
Natural resources that cannot be sustainably used because of improper use include:
- orests: Forests cover 31% of the Earth’s surface, sprawling across 4.06 billion hectares. It is not only the source of raw materials for paper and furniture but also enormously beneficial for fostering biodiversity and mitigating climate change. However, according to a report by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), deforestation from 1990 to 2020 has resulted in the vanishing of 420 million hectares of forest. Despite reductions in the rate of deforestation in recent years, as much as 10 million hectares of forest are disappearing annually.
- Marine fish: According to the statistics of the FAO, the problem of overfishing has become more serious every year, from 10% in 1974 to 35.4% in 2019. Unsustainable fishing accounts for one-third of all fish species, and only 10% of fish species have not yet reached the fishing quotas. As a result, the number of fishing vessels has increased without a corresponding growth in the catch. To make a living, fishermen are forced to engage in more aggressive fishing techniques such as taking risks in fishing in restricted areas, using illegal fishing gear, and underreporting catches. These will further exacerbate the depletion of natural fish resources.
- Soil: Microorganisms in the soil gradually transform organic pollutants into harmless organic substances or nutrient-rich humus that are beneficial for plant growth. When contamination is produced faster than the soil’s cleansing capability, the natural dynamic balance in the soil will be disrupted, resulting in the accumulation of contaminants that are not conducive to microorganism survival, in turn rendering the soil’s self-cleansing function useless. At the same time, the soil requires time to restore its fertility. The highly commercialized agricultural model of today deprives the soil of time to recover, while infertile soil will no longer facilitate plant growth, ultimately resulting in soil desertification. The UN’s statistics indicate that 12 million hectares of land are completely unfit for cultivation.
- Air: Airflow and rainfall will continue to deposit contaminants onto the ground, which are absorbed by the soil to cleanse the atmosphere. Also, plants can help to absorb toxic substances in the air. However, the large amount of waste gases generated by industrialization and transportation has caused soil desertification and forest fires that in turn create more dust, thereby overwhelming the natural purification ability of air and deteriorating air quality.
Non-renewable
The following are examples of non-renewable natural resources:
- Fossil fuels: When animal carcasses and dead plants are buried in the ground, fossil fuels will be formed after millions of years of high-temperature and high-pressure reactions. These include coal, oil, natural gas, and shale oil. However, the industrial revolution started only a few centuries ago, and there is no way we can wait for new fossil fuels to be generated.
- Minerals: The mineralization cycle is measured in hundreds of millions of years. The manufacturing of daily necessities such as cars, houses, wires, cell phones, and computers relies heavily on these minerals. Consequently, people must recycle non-renewable resources as much as possible.
What are examples of sustainable natural resources?
Sunlight
The sun constantly radiates light and heat energy. The energy that reaches the earth from the sun in a year is staggering, equivalent to double that of all fossil fuels and uranium reserves on the planet. Therefore, sunlight is truly an inexhaustible source of energy.
Geothermal heat
Geothermal heat originates from the lava inside the Earth, which reaches the ground through the flow of lava and groundwater. Currently, the speed at which geothermal energy is conducted to the ground is much faster than the speed of consumption by people, making it a sustainable natural resource.
Permaculture plants
Plants undergo photosynthesis using solar energy, breaking down water into oxygen and generating energy for carbon reactions in the process, eventually forming starch for animals to consume. Growing plants sustainably while taking soil fertility into account turns plants into a sustainable natural resource.
What is the importance of sustainability?
For the next generation
Excessive use of resources without consideration for sustainability will result in the deterioration of living conditions for the next generation, including natural disasters, rising prices, and health problems. This is unfair to future generations, in turn exacerbating intergenerational inequality and hostility.
For ourselves
Besides considering the ethical factors of the next generation and other people, sustainability is also extremely important to us. After all, the adverse consequences of unsustainability have manifested themselves within several decades or even several years. In addition to improving the environment, sustainability also creates a safety net for us, reducing the use and investment of natural resources that may be exhausted one day will decrease our reliance on them.
Why is the sustainable use of natural resources important?
Rising prices
If we can use natural resources in a sustainable manner and maintain a sufficient supply of natural resources, we will be able to prevent rising prices caused by scarcity or shortage of raw materials. For example, according to The Economist’s statistics, the price of wild fish has nearly doubled from 1990 to 2012, while the price of farmed fish has only increased by one-fifth. This trend will become more evident with overfishing.
Climate change
Using non-renewable natural resources will entail the destruction of the Earth’s ecological balance. When we extract and burn fossil fuels that took millions of years to form, greenhouse gases are released into the atmosphere. Overusing soil and forests will decrease vegetation on Earth, resulting in insufficient carbon sinks to absorb CO2. Climate change will cause more natural disasters to forests and make the sustainable use of natural resources more challenging.
Destruction of ecosystems
Ecosystems are delicate systems whose sustainability relies on the dynamic balance of various species of organisms. Non-sustainable use of the soil and forests will lead to habitat destruction, and overfishing will destroy ecological balance directly. These actions will cause the number of surviving species on Earth to diminish over time, and when the balance is completely lost, it will destroy entire ecosystems.
Food crisis
Although the current food supply is sufficient for the global population, with increasing population and the degradation of farmland, food crises may propagate from regions with high climate risks such as Africa, South Asia, as well as Central and South America, to affect people’s fundamental food needs.
Health risks
Air pollution and shortage of clean water are caused by the non-renewable use of air and water. Also, petrochemical plastics produced from non-renewable resources cannot be completely broken down in the environment. As a result, they will release microplastics into the ocean, streams, and other water cycles, and finally be consumed by us, in turn endangering our health.
Ways for businesses to achieve sustainable use of natural resources
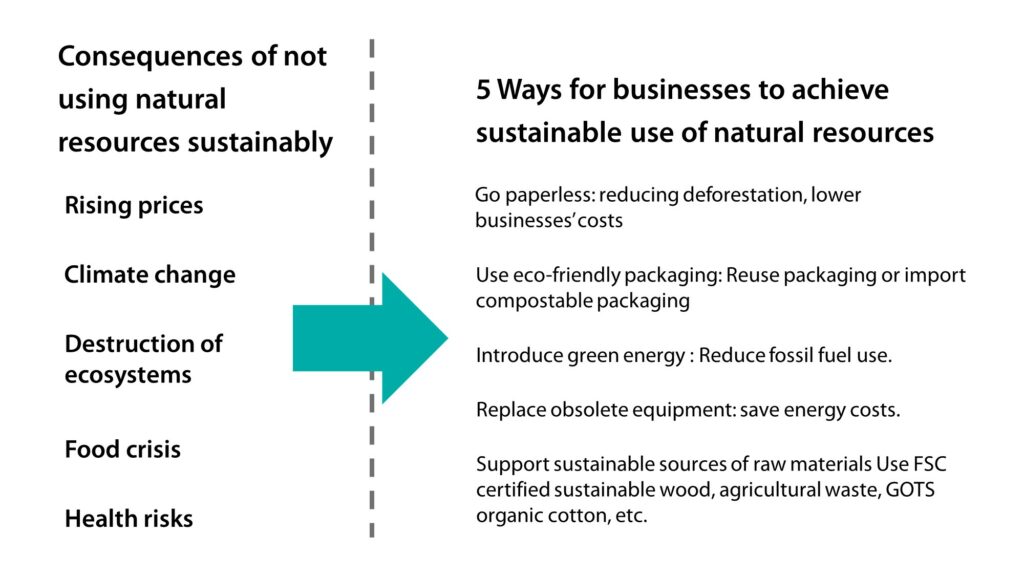
Go paperless
With new advances in technology, computers and server systems are becoming increasingly reliable. The power used for storing a document on the computer memory is far less than the consumption of natural resources by felling trees, making paper, and printing with ink. At the same time, paperless operations also lower businesses’ costs and facilitate data searches.
Use eco-friendly packaging
As far as the manufacturing and retail industries are concerned, packaging is a key issue because processes such as raw material transportation, production, and retail all rely on packaging. Businesses can reuse packaging. For instance, the packaging of imported raw materials can be saved, processed, and given to downstream manufacturers. Alternatively, packaging made of renewable materials such as recycled cardboard boxes and renouvo bagasse bags can be introduced. These types of eco-friendly packaging can be recycled or composted after use to reduce the use of natural resources by regenerating them into new products or returning them to the environment.
Introduce green energy
At present, the energy supply in most regions comes from burning fossil fuels. Purchasing green electricity or installing green energy facilities in enterprises can support the green energy industry effectively. In doing so, we can replace non-renewable natural resources with renewable resources, thereby lowering greenhouse gas emissions and preventing the fluctuating prices of fossil fuels from affecting enterprises’ costs. Currently, the RE100 international certification aims to achieve the goal of 100% green electricity by 2050, but many participating enterprises are striving to realize this objective in advance by 2030.
Replace obsolete equipment
As technology advances, equipment efficiency is also gradually improved. Therefore, replacing obsolete equipment can cut down energy consumption from the source and save energy costs for enterprises.
Support sustainable sources of raw materials
When purchasing raw materials or necessities, enterprises can give priority to selecting sustainable raw materials such as Forest Stewardship Council® (FSC®)-certified wood products, and compostable plastics made of agricultural waste including bagasse or coffee grounds. Furthermore, they can use Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS)-certified organic cotton to support the sustainable use of natural resources.
The future for the sustainable use of natural resources
The problems associated with our failure to use natural resources sustainably are gradually becoming visible. How to think ahead several years or several decades into the future, use natural resources sustainably through reduction, replacement, and recycling, reduce our need for non-renewable resources, as well as fostering sustainable fishing and forestry via sustainable management approaches, in order to minimize the burden on the soil and air have become urgent issues that people must face today.














